Efficiency and sustainability: they are perhaps the most important pillars in any business today. The government, as well as customers, shareholders and society demand thoughtful sustainability policies and transparent reporting from companies.
Sustainable processing of waste is an important spearhead. Imagine if your waste materials were valuable raw materials for others or if you yourself utilized the value of secondary raw materials in your product. This is how we open the door to a world in which sustainability and efficiency go completely hand in hand. Are you already taking steps towards a circular economy? Milgro helps your company and ensures the right match with the best processing method, processors and recyclers.
The importance of the right processing
We all know it: our planet is struggling with a growing amount of waste. It must be reduced. We let valuable resources degenerate into waste at lightning speed. This has consequences for all that lives on earth and for the available resources. We see this every year on Earth Overshoot Day.
To prevent raw materials from becoming waste, proper processing is important. Milgro is fully committed to this. By keeping valuable raw materials longer in the chain and minimizing pollution from waste, we relieve the pressure on natural resources. Cooperation with waste processors is therefore not only meaningful for the here-and-now, but also for a future-oriented view.
Choosing the right processing method
A circular economy seeks to preserve the value of raw materials by not allowing them to become waste. For many companies, this starts with carefully selecting the right processing methods for the waste streams a company produces. For each waste stream, Milgro looks for the best method. We pay attention to ecology, but also to service, location and cost.
Milgro takes an independent position. Thus, we make the right match between your waste streams, the optimal processing methods and the best processors in our extensive network. We keep testing this match continuously. In this way, we continuously guarantee that your company benefits from the best solution.
Recycling
Recycling refers to the conversion of waste materials into secondary raw materials or products. This starts with the separate collection of waste materials, such as paper, glass, plastics and metals. Based on their composition and properties, the waste materials undergo various treatment processes. Examples include grinding, melting, washing or chemical treatment. This creates secondary raw materials or materials.

Although recycling reduces the need for virgin raw materials, recycling does require energy, water and often auxiliary materials. Also, not all materials are suitable for recycling, and many products are assembled in such a way that materials cannot be separated and recycled. And then there is almost always some loss of quality as well. This is why recycling ranks fairly low on the R-ladder.
Composting
Composting is the process of converting organic waste, such as food scraps and garden waste, into compost. Compost provides a rich nutrient base for horticulture and agriculture. Microorganisms break down the organic waste. They convert it into a dark, crumbly substance rich in nutrients for plants.
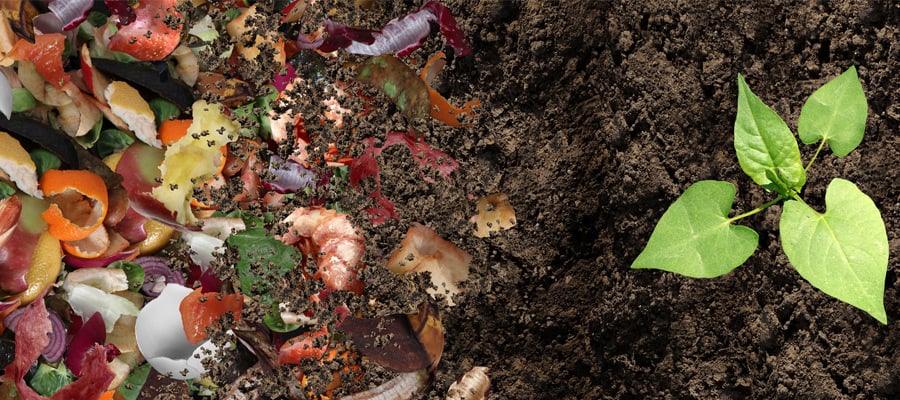

Composting fits into a circular economy. Organic waste is converted into valuable raw materials for new growth. It creates a natural, sustainable fertilizer for agriculture. At the same time, it reduces the amount of waste.
Incineration
Incineration: burning waste at high temperatures to generate energy. Although incineration generates energy, in the process you destroy the value of raw materials. Therefore, we really consider incineration the very last option for processing. Poor management can also have negative consequences. Consider air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
Biomass
Biomass is organic material derived from all plant and animal resources, such as wood, pruning waste and sewage sludge. Burning biomass generates heat. In addition, biomass is converted into liquid fuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel. Biomass reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
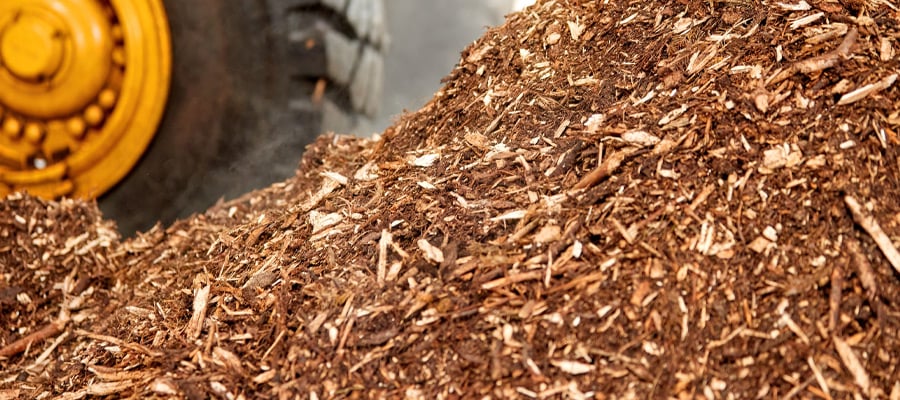

Because living organisms can renew themselves naturally, we consider biomass a renewable energy source. Biomass can potentially be carbon neutral: the CO2 released during combustion is reabsorbed by existing plants. However, this depends on how quickly the used vegetation is replaced. In practice, burning biomass can lead to significant CO2 emissions. This is especially true when reforestation is not managed efficiently.
Fermentation
In fermentation, bacteria and fungi convert biomass into biogas, also known as green gas. In this method, biomass is converted to alcohol, lactic acid, methane and CO2, among others.
Fermentation efficiently converts organic waste into valuable sources of energy. In this way, dependence on fossil fuels is reduced. The by-product of fermentation is digestate, which can be used as fertilizer. However, it is important that fermentation is done properly to prevent the release of potentially harmful substances, such as ammonia.

Distilling
Distillation is a separation technique in which a liquid mixture is evaporated, separating one or more components. Distillation is widely used in the production of spirits, for example to separate alcohol from water. The petrochemical industry also employs distillation to separate different fractions of crude oil.
Distillation can play an important role in the circular economy. For example, in recovering or reusing valuable materials from waste streams. Consider solvent recycling or chemical recovery.
Animal Feed
Rejected food or waste streams from food production are often used as animal feed. Think of agricultural by-products, unsold food products or food waste from households and restaurants. This actually prevents a residual steam from becoming waste but labels the product as raw material for animal feed. To ensure food safety, the discarder must meet GMP+ certification requirements.
By making these products ingredients of animal feed, food waste is minimized. At the same time, we increase the value of these residual streams. This is a great example of a closed chain in the circular economy.
Food for Food
Food waste or food by-products can also serve as ingredients for new food products. Waste streams or surpluses are thereby converted into valuable ingredients. Consider using leftover grains from beer brewing to make bread. Making cake bottoms from cookie cuttings. Or reusing fruit and vegetable pulp for new foods.
Food for Food minimizes food waste and maximizes the value of residual streams. This creates a more sustainable chain of food production.

Working with Milgro on the most sustainable processing method
How do you ensure the most sustainable processing method for each waste stream within your company? Milgro's experts are happy to advise on the most sustainable processing method. From our independent position, we look for the right processor from our large network. We also pay attention to the costs.
And that is not all. We periodically check whether improvements are possible. We also look at processing methods. In case of improvement proposals, we consult with our client about which optimizations should be given priority. We also consider the expected CO2 impact. When these optimizations are realized, our clients benefit from the gains in eco, euro and service. Meanwhile, the market for processing does not stand still. We are working hard on innovations and solutions for circularity. We follow these developments closely, so that our clients can benefit from them.
Learn more.
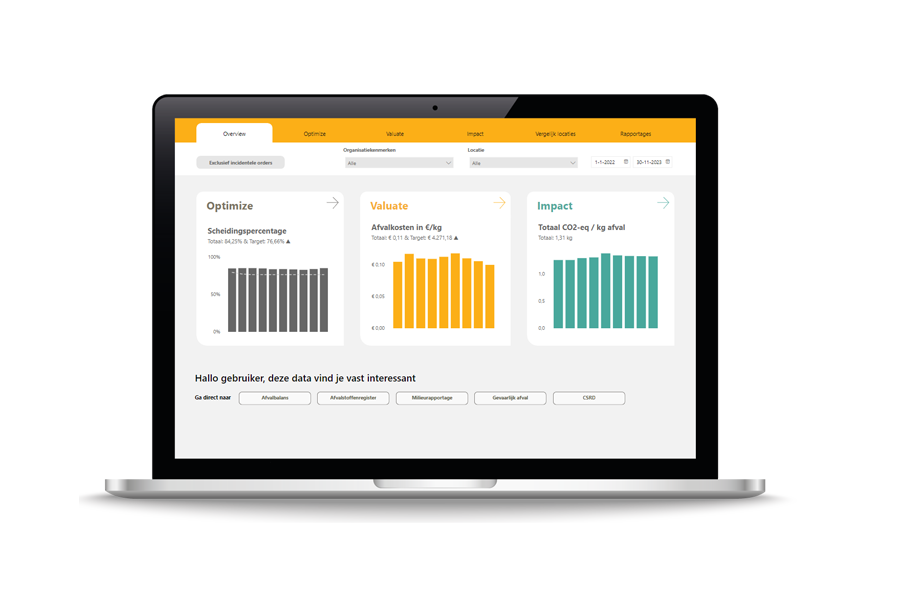
The Milgro dashboard provides you with a comprehensive overview of the processing methods of all your waste streams. With the corresponding performance in terms of ecology and costs. Are you curious about the possibilities of our dashboard? Then book a no-obligation demo with one of our consultants.
Stay informed
Stay up to date on all new developments? Follow us on LinkedIn or Instagram. Or subscribe to the newsletter. Are you curious about what Milgro can do for your operations and waste process? Contact us












